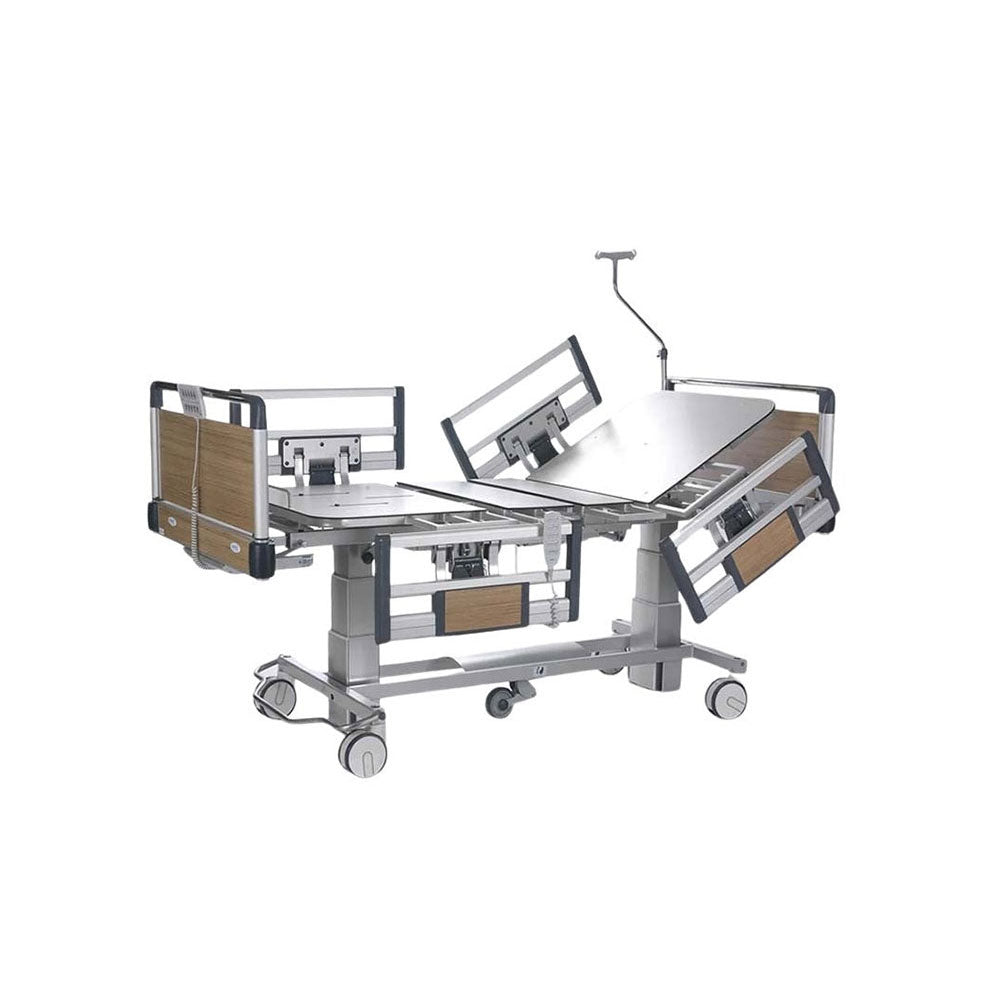
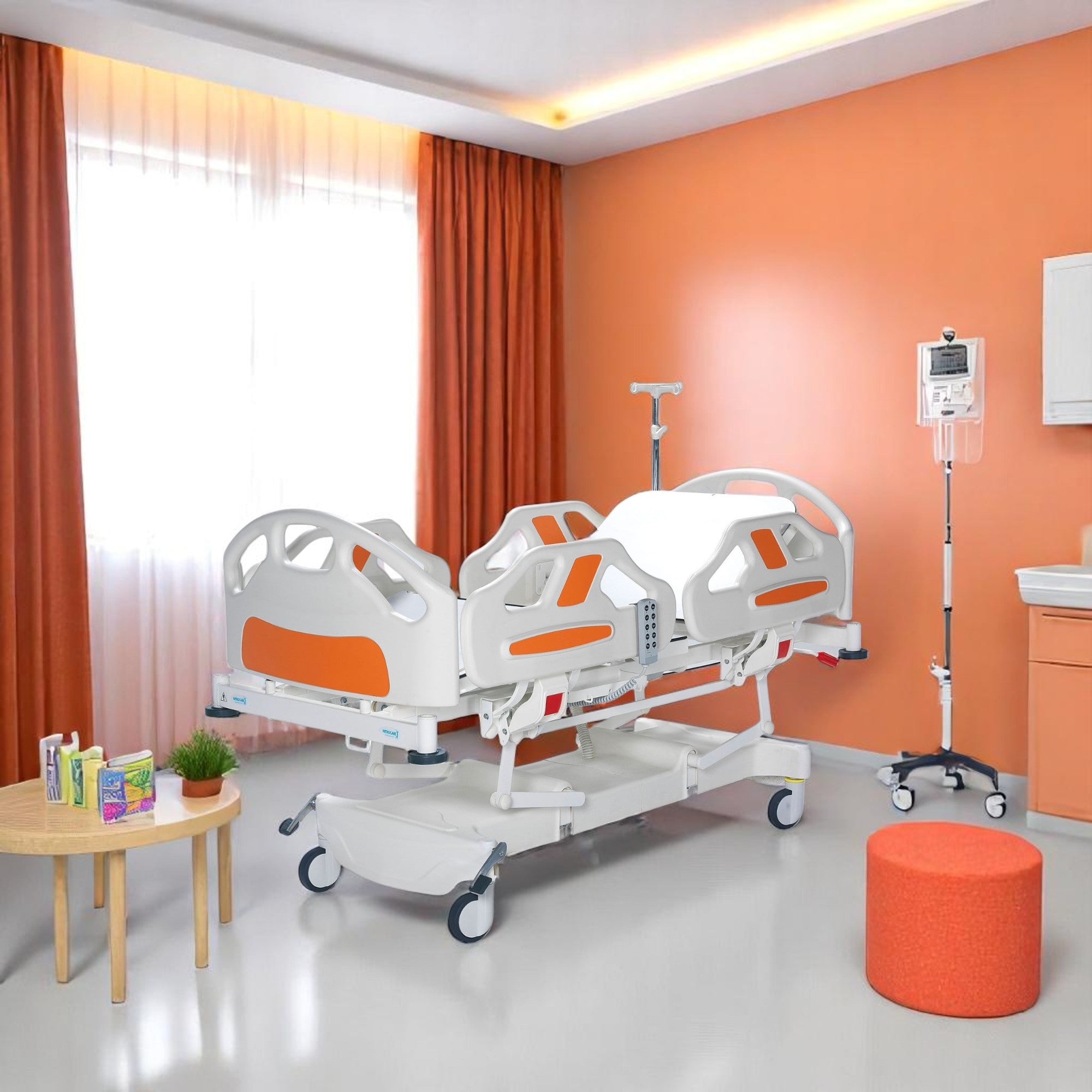
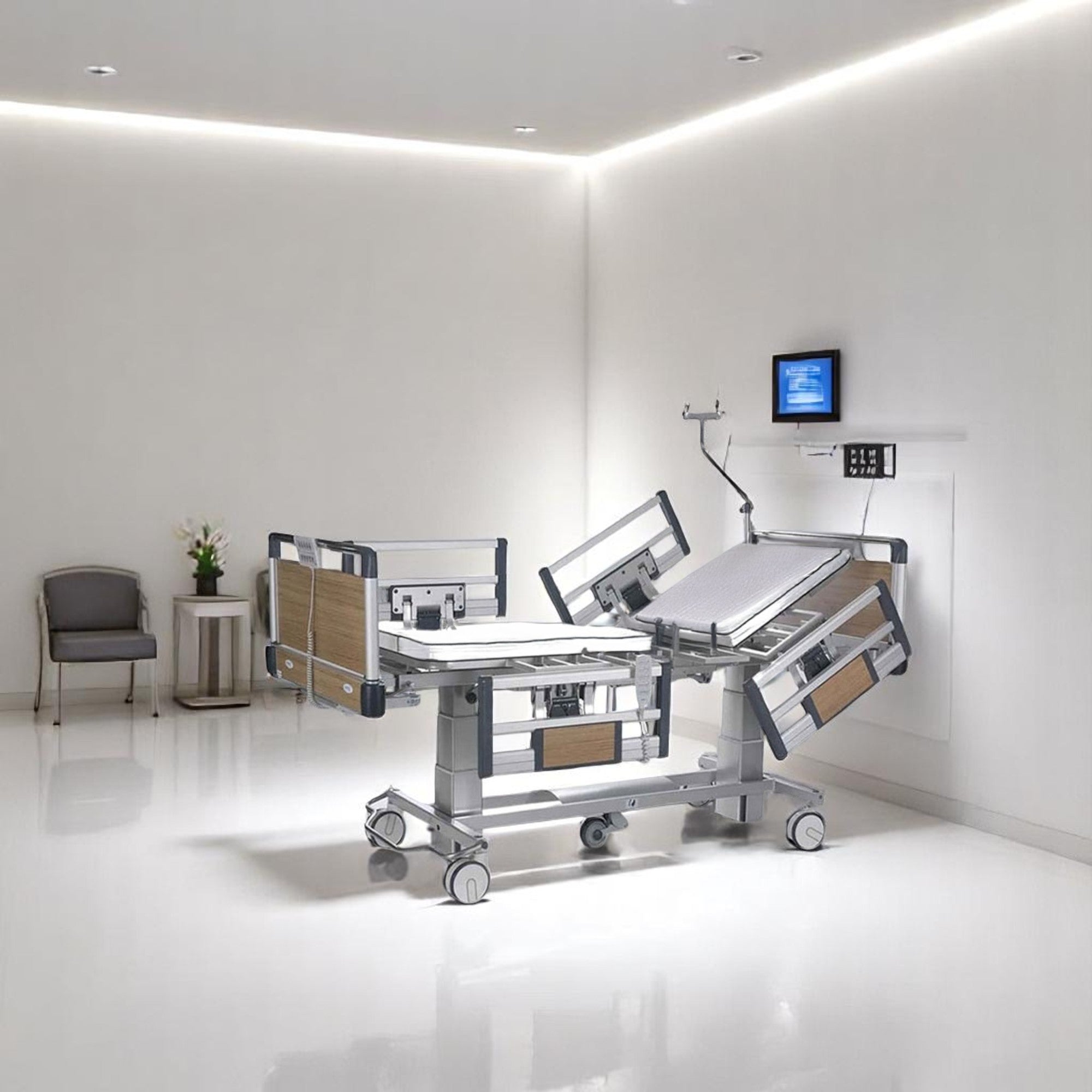
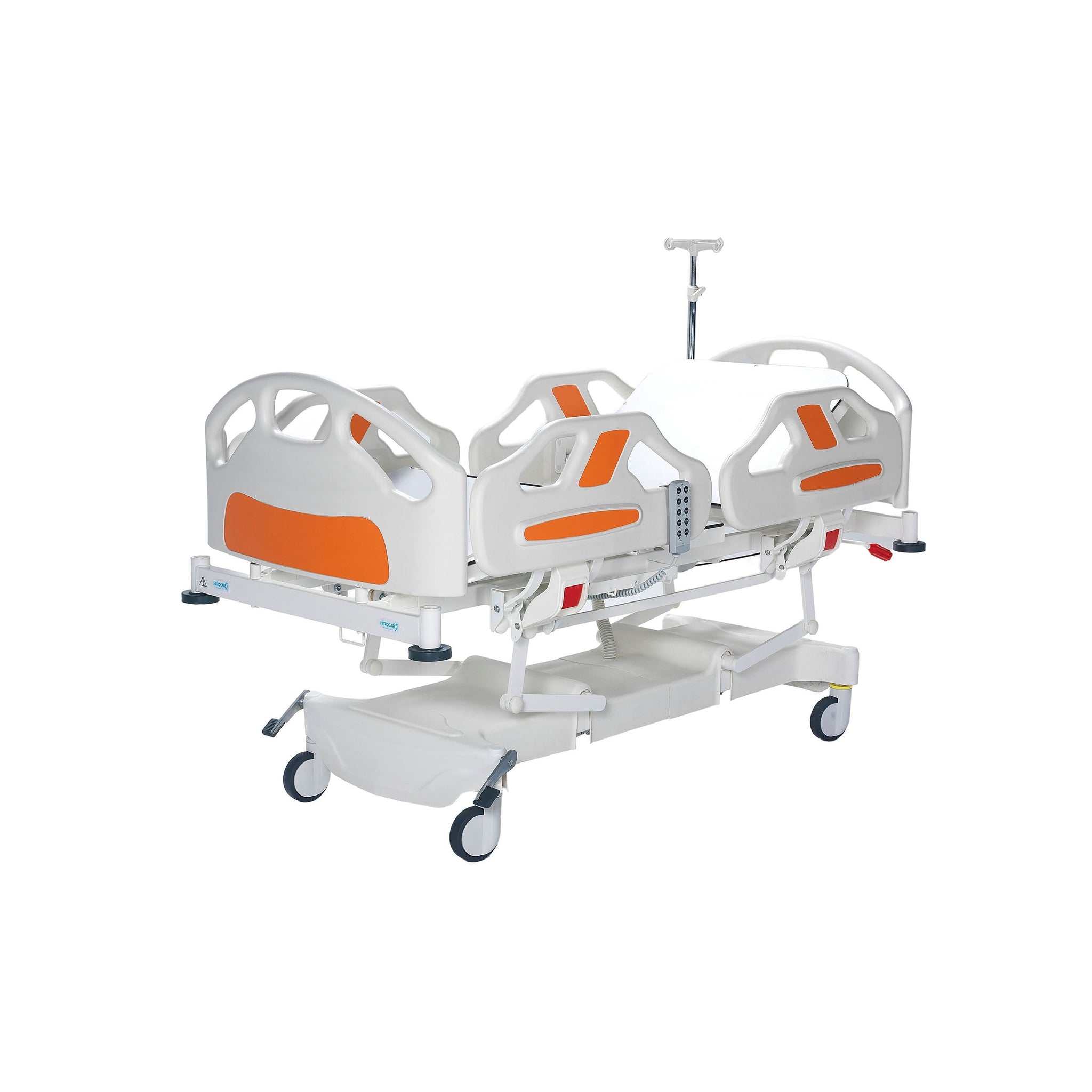
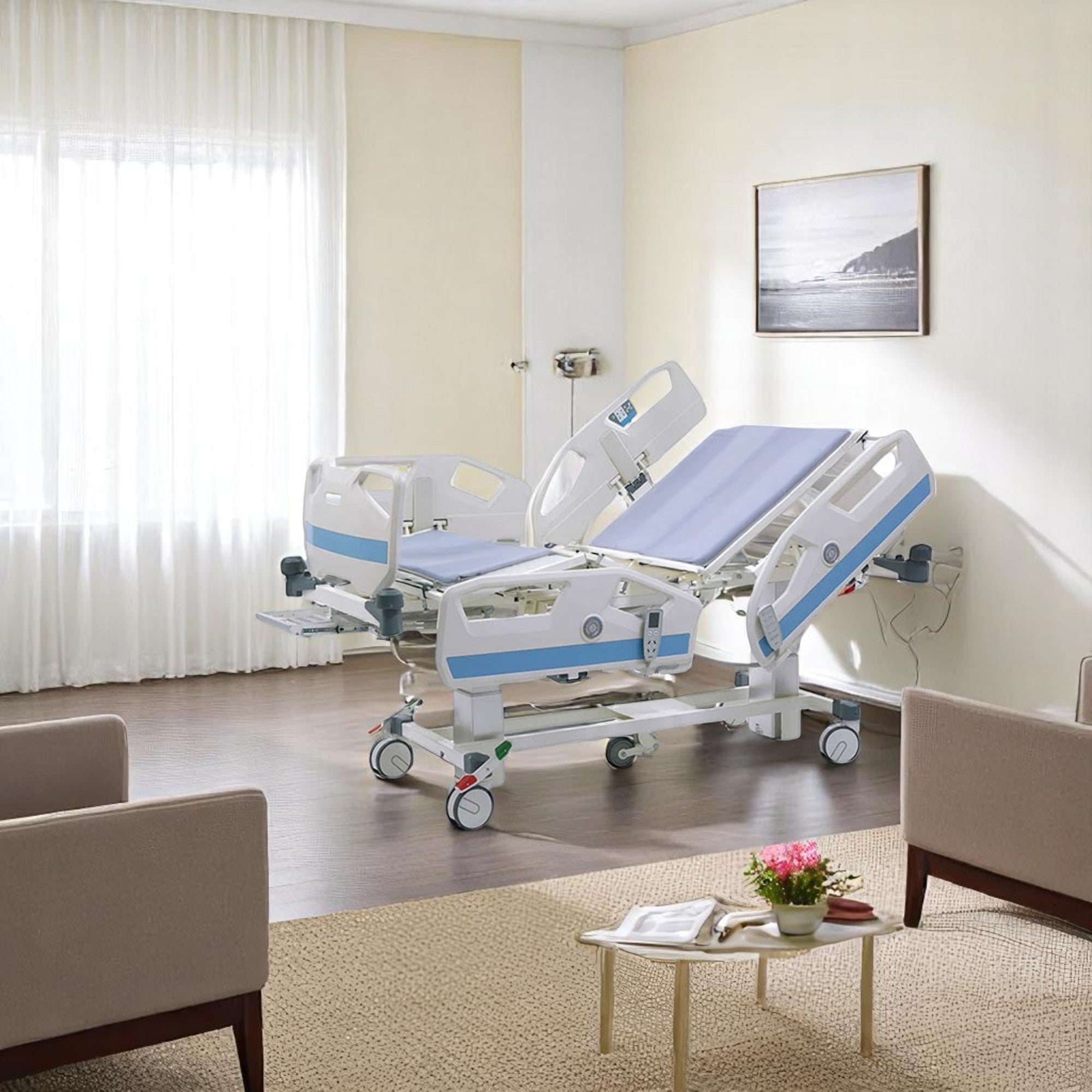
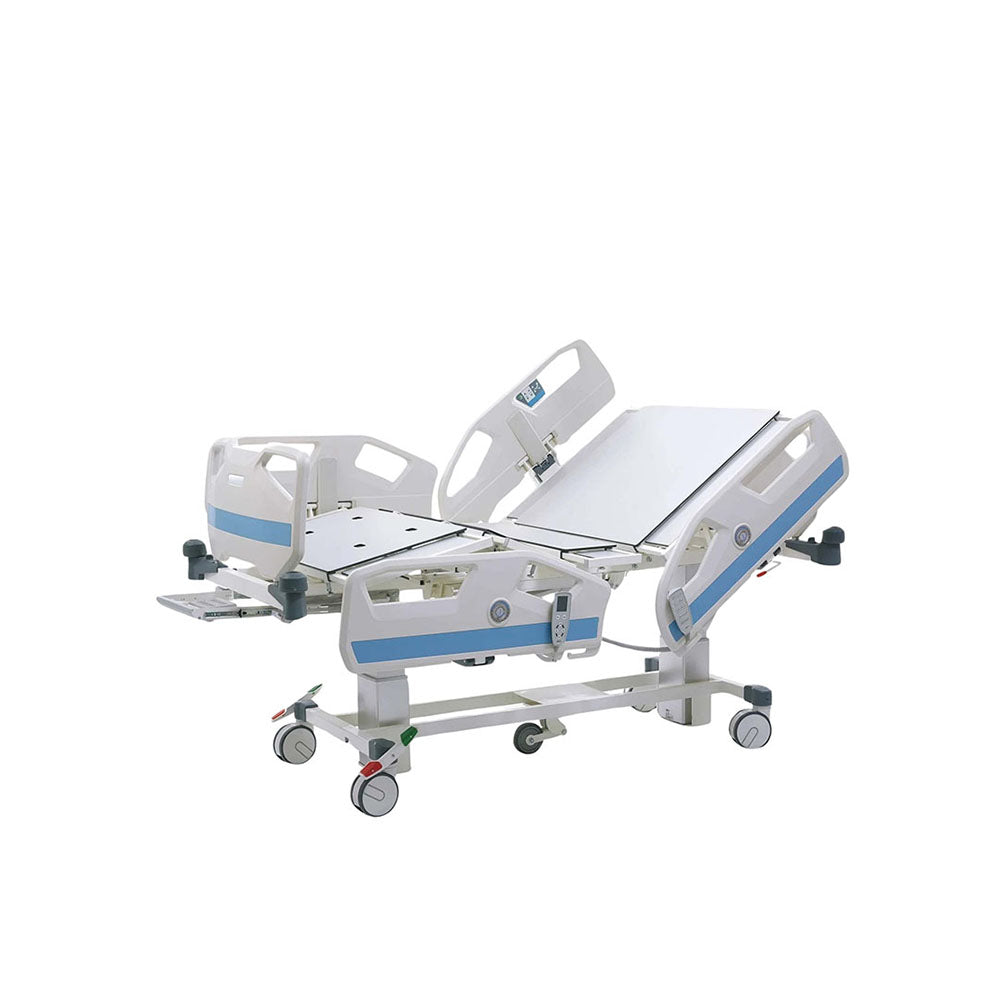
Hospital Beds
Medical beds can be electric and motorized, with the ability to adjust the head of the bed up and down as well as tilt it back so that an individual can sit up on their own. Hospital beds are made out of metal frames which support one or two mattresses. We at Rescue Supply carry a series of patient beds, each designed to keep individuals secure while improving accessibility to key vital points for doctors. Shop our collection of hospital beds below to find the right models to suit your particular needs.

You may also like:
Nitrocare Fortis 6220: Full Electric Bariatric ICU Bed with Integrated Scale and Lateral Tilt
Factory Direct Ships 2-3 Days! (Estimated) More infoYou may also like:
Nitrocare Pippa 4420P: Full Electric Pediatric Bed with Side Rail Safety Locks
Factory Direct Ships 2-3 Days! (Estimated) More infoYou may also like:
Nitrocare Vigora 4220: Full Electric Bariatric ICU Bed with Integrated Weighing System
Factory Direct Ships 2-3 Days! (Estimated) More infoYou may also like:
Nitrocare Senna 4430P: Full Electric Pediatric ICU Bed with Integrated Nursing Controls
Made to Order Ships in 10-12 Weeks! (Estimated) More infoFrequently Asked Questions
Find answers to commonly asked questions below.
-
Can you buy hospital beds for home?
Yes, you can absolutely buy hospital beds for home use, and they are widely available through medical supply stores, online retailers, and local durable medical equipment providers. These beds are designed to provide comfort, safety, and support for individuals recovering from surgery, managing chronic conditions, or requiring long-term care. Home hospital beds often come with adjustable features, side rails, and specialized mattresses to prevent bedsores and improve patient positioning. Purchasing a hospital bed for home can significantly enhance caregiving by reducing strain on caregivers and improving patient mobility. Many suppliers offer rental options if you only need the bed temporarily, which can be cost-effective. Before buying, consider the patient’s medical needs, available space, and whether insurance or Medicare will cover part of the cost.
-
What is the difference between a hospital bed and an adjustable bed?
A hospital bed is specifically designed for medical care, offering advanced features like adjustable height, head and foot sections, side rails, and compatibility with medical accessories such as IV poles and overbed tables. These beds prioritize patient safety and caregiver convenience, often including wheels for mobility and locking mechanisms for stability. In contrast, an adjustable bed is primarily intended for comfort and lifestyle use, allowing users to raise or lower the head and foot sections for better sleep posture or relaxation. Adjustable beds typically lack medical-grade safety features like side rails and emergency positioning options such as Trendelenburg or cardiac chair positions. While both types of beds provide adjustability, hospital beds are built for clinical needs, whereas adjustable beds focus on comfort and luxury. Choosing between the two depends on whether the primary goal is medical care or enhanced sleep comfort.
-
How to get a hospital bed at home?
Getting a hospital bed at home involves several steps, starting with assessing the patient’s medical needs and space availability. You can purchase or rent a hospital bed from medical supply companies, home healthcare providers, or online retailers specializing in durable medical equipment. If the bed is medically necessary, check with your doctor for a prescription, as this can help with insurance or Medicare coverage. Many suppliers offer delivery and setup services, ensuring the bed is properly installed and safe for use. Consider additional accessories like pressure-relief mattresses, side rails, and overbed tables to enhance comfort and functionality. If cost is a concern, rental options or refurbished beds can provide affordable alternatives. Always confirm the bed’s weight capacity, adjustability features, and ease of cleaning before making a decision.
-
What are the three types of medical beds?
The three main types of medical beds are manual, semi-electric, and fully electric beds. Manual hospital beds require physical effort to adjust the head, foot, and height positions using hand cranks, making them the most affordable option but less convenient for caregivers. Semi-electric beds combine electric controls for head and foot adjustments with manual height adjustment, offering a balance of cost and ease of use. Fully electric beds provide complete adjustability through a remote control, including height, head, and foot sections, which greatly reduces caregiver strain and enhances patient comfort. Some advanced models also include specialized positions like Trendelenburg or reverse Trendelenburg for improved circulation and respiratory support. Choosing the right type depends on the patient’s mobility, caregiver availability, and budget.